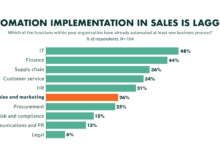
Best Enterprise CRM Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
Best Enterprise CRM Solutions are crucial for large organizations seeking to streamline operations and enhance customer relationships. This guide delves into the complexities of choosing, implementing, and maximizing the value of an enterprise CRM system. We’ll explore key features, leading vendors, and future trends, providing a comprehensive overview for businesses navigating the world of enterprise-level customer relationship management.
From defining your specific needs and evaluating different deployment models to understanding the intricacies of integration with other business systems, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions. We will analyze top vendors, comparing their strengths, weaknesses, and pricing structures, ultimately assisting you in selecting the solution that best aligns with your organizational goals and budget.
Defining Enterprise CRM Needs
Enterprise CRM systems are significantly different from solutions designed for smaller businesses. The scale, complexity, and integration requirements necessitate a more robust and adaptable approach. This section delves into the specific needs and characteristics that define an effective enterprise CRM solution.
Enterprise CRM systems manage vast amounts of customer data, interactions, and sales processes across multiple departments and potentially global locations. Unlike smaller business solutions which might focus on simple contact management and sales tracking, enterprise CRMs require sophisticated functionalities to handle the complexities of large-scale operations.
Key Differences Between Enterprise and Small Business CRM
Enterprise CRM solutions are characterized by their scalability, advanced functionalities, and integration capabilities. They support a far greater number of users and data points than smaller systems, offering features like advanced analytics, workflow automation, and robust security protocols tailored to large organizations’ regulatory compliance needs. Small business CRMs, on the other hand, often focus on simpler features and user interfaces, prioritizing ease of use over extensive customization and integration. The cost also reflects this difference, with enterprise systems requiring a larger initial investment and ongoing maintenance.
Typical Functionalities of Enterprise CRM Systems
A comprehensive enterprise CRM typically incorporates a wide array of functionalities. These include: customer relationship management (contact management, lead management, opportunity management, sales forecasting), marketing automation (campaign management, email marketing, social media integration), customer service and support (case management, knowledge base, self-service portals), sales force automation (territory management, quota tracking, commission calculations), and comprehensive reporting and analytics dashboards providing real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs). Furthermore, advanced features like predictive analytics, AI-powered insights, and integration with other business systems are often crucial components of a robust enterprise CRM solution.
Integration Needs of Enterprise CRM
Successful enterprise CRM deployment relies heavily on seamless integration with other core business systems. Integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems ensures consistent data flow between sales, marketing, and operations. This avoids data silos and provides a holistic view of the customer journey and business operations. Similarly, integration with marketing automation platforms streamlines marketing campaigns, tracks campaign effectiveness, and facilitates personalized customer interactions. Other important integrations might include customer support ticketing systems, e-commerce platforms, and data warehousing solutions for advanced analytics and reporting. The degree of integration required will depend on the specific needs and complexity of the organization.
On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Enterprise CRM Deployment
The choice between on-premise and cloud-based deployment significantly impacts cost, scalability, and security.
| Deployment Model | Cost | Scalability | Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Premise | High initial investment, ongoing maintenance costs, IT infrastructure expenses. | Limited scalability; requires significant upfront planning and investment for future growth. | High level of control over data and security infrastructure; however, requires dedicated IT resources to manage security updates and patches. |
| Cloud-Based | Lower initial investment; subscription-based model with predictable monthly or annual costs. | Highly scalable; easily adjust resources based on business needs without significant infrastructure changes. | Relies on the vendor’s security infrastructure and expertise; requires careful evaluation of the vendor’s security policies and compliance certifications. |
Top Enterprise CRM Vendors
Choosing the right enterprise CRM solution is crucial for business success. The market offers a wide array of options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the key players and their offerings is paramount to making an informed decision. This section will delve into some of the leading vendors, comparing their features, pricing, and overall suitability for different enterprise needs.
Leading Enterprise CRM Vendors
Several vendors dominate the enterprise CRM landscape. These include Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SAP CRM. While other significant players exist, these three consistently rank among the top choices for large organizations due to their comprehensive features, robust scalability, and extensive market presence. Their solutions cater to diverse industry verticals and organizational sizes.
Comparison of Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SAP CRM
Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SAP CRM each offer powerful enterprise-grade CRM solutions, but their strengths and weaknesses differ significantly.
| Feature | Salesforce | Microsoft Dynamics 365 | SAP CRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Strength | Extensive AppExchange ecosystem, highly customizable, strong sales force automation | Seamless integration with other Microsoft products, robust reporting and analytics, strong customer service capabilities | Deep integration with other SAP enterprise applications, excellent for complex business processes, strong in supply chain management |
| Weakness | Can be expensive, complex to implement, steep learning curve | Customization can be challenging compared to Salesforce, may require significant IT expertise | Can be complex and expensive, implementation can be lengthy, less flexible than Salesforce |
Pricing Models and Licensing Options
Each vendor offers various pricing models and licensing options, typically based on the number of users, features included, and support levels required. Salesforce often utilizes a subscription-based model with tiered pricing plans, while Microsoft Dynamics 365 employs a similar structure, offering different licenses for specific modules (e.g., Sales, Service, Marketing). SAP CRM typically follows a more traditional licensing model, often involving upfront costs and ongoing maintenance fees. Specific pricing details vary greatly depending on the chosen features and contract terms. Detailed quotes are usually necessary to determine the exact cost for a specific organization’s needs.
Key Features and Unique Selling Propositions
Understanding the unique features of each vendor is critical for selecting the best fit.
Salesforce:
- Extensive AppExchange marketplace for customization and extensions.
- Powerful sales cloud with robust lead management and opportunity tracking.
- Strong community support and extensive documentation.
- Unique Selling Proposition: Unmatched ecosystem and flexibility for customization.
Microsoft Dynamics 365:
- Seamless integration with Microsoft Office 365 and other Microsoft products.
- Robust reporting and analytics capabilities for data-driven decision making.
- Excellent customer service features including case management and knowledge bases.
- Unique Selling Proposition: Deep integration within the Microsoft ecosystem.
SAP CRM:
- Deep integration with other SAP enterprise applications, enabling end-to-end process automation.
- Robust capabilities for managing complex business processes and supply chains.
- Strong focus on enterprise resource planning (ERP) integration.
- Unique Selling Proposition: Comprehensive integration with existing SAP systems.
CRM Features & Functionality
A robust Enterprise CRM system is more than just a contact list; it’s a multifaceted tool designed to streamline operations, improve customer relationships, and ultimately drive revenue growth. Its core functionality revolves around several key modules, each playing a crucial role in achieving these objectives. Effective integration between these modules is key to unlocking the full potential of the system.
Contact Management
Effective contact management is the bedrock of any successful CRM strategy. A centralized database allows businesses to store and access comprehensive information about each customer interaction, from initial contact details to purchase history and communication preferences. This holistic view empowers sales, marketing, and customer service teams to personalize interactions, anticipate needs, and build stronger relationships. Features such as segmentation based on demographics, purchase behavior, or engagement levels enable targeted marketing campaigns and tailored customer service experiences. For example, a company could segment customers based on their purchase frequency to offer loyalty programs to high-value customers, or offer targeted promotions to those who haven’t purchased recently. This detailed understanding of the customer journey significantly enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Sales Force Automation
Sales force automation (SFA) modules within an enterprise CRM automate and streamline various sales processes, boosting efficiency and productivity. Features such as lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting provide sales teams with real-time insights into their performance and pipeline health. Automated workflows, such as email reminders for follow-ups or notifications for critical milestones, reduce manual tasks and ensure that no potential sales opportunities are missed. For instance, automated email sequences triggered by specific customer actions can nurture leads and increase conversion rates. Real-time dashboards displaying key sales metrics provide a clear overview of performance, enabling quick identification of areas for improvement and strategic adjustments.
Customer Service Modules
Effective customer service is critical for customer retention and building brand loyalty. CRM systems equipped with customer service modules centralize all customer interactions, providing a single source of truth for agents. This allows agents to access a complete customer history, including past interactions, purchase history, and support requests, enabling them to provide personalized and efficient support. Features such as ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and integrated chatbots streamline the resolution of customer issues and improve response times. For example, a company can use a knowledge base to provide self-service options for common issues, reducing the workload on customer service agents and improving customer satisfaction. The integration of these tools allows for seamless escalation of issues when necessary, ensuring efficient handling of complex problems.
Reporting and Analytics Dashboards
Reporting and analytics dashboards provide valuable insights into business performance across various areas. These dashboards visualize key metrics, such as sales conversion rates, customer churn, and customer lifetime value, enabling data-driven decision-making. By tracking these metrics, businesses can identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and measure the effectiveness of their strategies. For example, a decline in customer satisfaction scores might indicate a need for improved customer service training or process optimization. Similarly, a low conversion rate might highlight the need for improvements in the sales process or marketing campaigns. The ability to customize dashboards to display relevant metrics ensures that business leaders have access to the information they need to make informed decisions.
CRM Integration with Marketing Automation Tools
Integrating CRM with marketing automation tools significantly enhances the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. This integration allows for automated workflows based on customer behavior and preferences, leading to personalized and targeted marketing communications. For instance, a customer who abandons their shopping cart can receive an automated email reminder, while a customer who frequently purchases a specific product can receive personalized recommendations. This level of personalization enhances engagement and drives conversions. Marketing automation tools can also track campaign performance, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of various marketing strategies and enabling data-driven optimization.
Improved Customer Relationship Management and Increased Customer Lifetime Value
By providing a holistic view of the customer journey, CRM systems contribute significantly to improved customer relationship management (CRM) and increased customer lifetime value (CLTV). The ability to personalize interactions, anticipate needs, and provide timely and relevant support strengthens customer relationships, leading to increased loyalty and repeat business. Improved customer service and targeted marketing campaigns further enhance customer satisfaction, resulting in higher CLTV. For example, a company that proactively addresses customer issues and anticipates their needs is more likely to retain customers and increase their lifetime value. Furthermore, personalized marketing campaigns can drive repeat purchases and increase customer spending over time. The data-driven insights provided by CRM systems enable businesses to make informed decisions that optimize customer relationships and maximize CLTV.
Implementation & Integration
Implementing a large-scale enterprise CRM system is a significant undertaking, demanding careful planning, substantial resources, and a phased approach. The complexity arises from the sheer volume of data involved, the need for seamless integration with existing systems, and the potential disruption to business processes during the transition. Success hinges on meticulous project management, effective change management strategies, and a deep understanding of the organization’s specific needs.
Challenges in implementing a large-scale enterprise CRM system are multifaceted. Data migration from legacy systems can be time-consuming and error-prone, requiring robust data cleansing and transformation processes. Integration with existing applications, such as ERP, marketing automation, and e-commerce platforms, presents significant technical hurdles. Furthermore, user adoption is critical; resistance to change among employees can hinder the successful deployment and utilization of the new system. Finally, the cost of implementation, including software licensing, consulting fees, training, and ongoing maintenance, can be substantial.
Data Migration Best Practices
Effective data migration is crucial for a successful CRM implementation. This involves a multi-step process beginning with thorough data assessment and cleansing. Data quality is paramount; inaccurate or incomplete data will render the CRM system ineffective. A robust data mapping strategy is needed to ensure accurate transfer of information between the legacy system and the new CRM. Data validation and verification steps should be incorporated throughout the migration process to identify and correct errors. Finally, a phased migration approach, starting with a pilot group or a subset of data, can minimize disruption and allow for adjustments based on early experiences.
System Integration Strategies
Seamless integration with existing business applications is key to maximizing the value of a new CRM system. This can involve using application programming interfaces (APIs) to connect the CRM with other systems, enabling data exchange and automation of workflows. Enterprise service buses (ESBs) can also be employed to facilitate communication between disparate applications. Careful consideration should be given to data security and privacy during the integration process, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. Regular testing and monitoring are crucial to identify and resolve any integration issues that may arise.
Successful Enterprise CRM Implementations
Salesforce’s implementation at Adobe is often cited as a successful example. Adobe leveraged Salesforce’s platform to streamline its sales and marketing processes, improve lead management, and gain a more unified view of its customer base. Key success factors included strong executive sponsorship, a clear project roadmap, and a dedicated implementation team. Similarly, a company like Microsoft’s own internal CRM implementation, while likely complex, demonstrates the power of a well-executed project when integrating with existing internal tools and workflows. Their success likely hinges on internal expertise and iterative development, allowing for adaptation based on internal feedback.
Step-by-Step CRM System Integration Guide
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Define the scope of integration, identify target applications, and establish clear objectives.
- Data Mapping and Transformation: Map data fields between the CRM and existing systems, and develop data transformation rules to ensure consistency.
- API and Integration Strategy Selection: Choose appropriate integration methods (APIs, ESBs, etc.) based on technical capabilities and budget.
- Development and Testing: Develop integration components, conduct thorough testing, and address any identified issues.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Deploy the integrated system, provide user training, and monitor performance post-launch.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization: Continuously monitor system performance, address any issues, and optimize integration processes over time.
Future Trends in Enterprise CRM
The enterprise CRM landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements and evolving business needs. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage CRM for maximum efficiency and competitive advantage. This section explores key future directions in enterprise CRM, focusing on the impact of AI and data security, and providing a glimpse into its predicted evolution.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in CRM
AI and ML are revolutionizing CRM capabilities, moving beyond basic data management to offer predictive analytics and intelligent automation. AI-powered CRM systems can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict customer behavior, enabling proactive engagement and personalized experiences. For example, AI can predict customer churn risk, allowing businesses to intervene with targeted retention strategies. ML algorithms can automate repetitive tasks such as lead scoring and data entry, freeing up human agents to focus on higher-value activities. This increased efficiency leads to improved customer satisfaction and increased sales conversion rates. The integration of natural language processing (NLP) further enhances customer interactions through chatbots and virtual assistants, providing 24/7 support and instant responses. Companies like Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics 365 are already heavily investing in AI and ML integrations within their CRM platforms.
Data Security and Privacy in Enterprise CRM
With the increasing amount of sensitive customer data stored within CRM systems, data security and privacy are paramount. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA mandate stringent data protection measures, requiring businesses to implement robust security protocols to safeguard customer information. Future enterprise CRM solutions will prioritize data encryption, access control, and compliance with evolving privacy regulations. Furthermore, the focus will shift towards transparent data handling practices, empowering customers with greater control over their data. This includes providing users with clear visibility into how their data is collected, used, and protected. Investing in advanced security features such as multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits will be crucial for maintaining customer trust and avoiding costly data breaches.
Predicted Evolution of Enterprise CRM (Next Five Years)
A visual representation of the predicted evolution of enterprise CRM over the next five years would show a shift from primarily transactional systems to highly intelligent, personalized, and integrated platforms. Imagine a three-dimensional graph. The X-axis represents the level of AI integration, ranging from basic automation to advanced predictive analytics. The Y-axis depicts the level of data security and privacy measures, escalating from basic compliance to proactive, privacy-centric design. The Z-axis represents the degree of platform integration, ranging from siloed systems to seamless integration across all business functions. The graph would illustrate a clear upward trajectory across all three axes, showing a progressive increase in AI capabilities, security measures, and integration over the next five years. This represents a move towards CRM systems that are not only efficient but also ethical and customer-centric. For example, a company might start with basic AI-powered lead scoring and gradually implement predictive churn analysis and personalized marketing campaigns, while simultaneously strengthening data security measures and integrating CRM with its sales, marketing, and customer support platforms. This evolution reflects a continuous improvement in both functionality and responsible data handling.
Closing Notes
Selecting the right enterprise CRM solution is a significant undertaking, demanding careful consideration of various factors. This guide has provided a framework for evaluating your needs, exploring leading vendors, and understanding the future of CRM technology. By thoughtfully assessing your requirements and leveraging the insights shared, your organization can effectively harness the power of a robust CRM system to foster stronger customer relationships, drive business growth, and achieve lasting success.