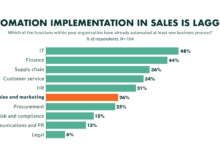
CRM Software for Small Business Success
CRM Software for Small Business is more than just software; it’s a strategic investment that can significantly impact growth and profitability. Effectively managing customer relationships is crucial for any small business, and a well-chosen CRM system provides the tools to streamline communication, track interactions, and ultimately, boost sales. This guide explores the essential aspects of selecting, implementing, and maximizing the benefits of a CRM tailored to the unique needs of small businesses.
From defining your specific requirements and exploring diverse software options to mastering implementation and measuring success, we’ll navigate the journey of leveraging CRM technology to cultivate stronger customer relationships and achieve sustainable growth. We’ll also delve into the future trends shaping the CRM landscape, ensuring you’re prepared for the evolving technological environment.
Defining Needs for Small Business CRM
Small businesses often face the challenge of juggling multiple responsibilities, and effective customer relationship management (CRM) is frequently overlooked amidst the demands of daily operations. This can lead to lost opportunities, decreased efficiency, and ultimately, hindered growth. Implementing a CRM system specifically designed for small businesses can address these challenges and provide a significant boost to productivity and profitability.
The typical challenges faced by small businesses in managing customer relationships include difficulties in tracking interactions, inconsistent communication across teams, inefficient lead management, and a lack of centralized customer data. This fragmented approach can lead to a poor customer experience, missed sales opportunities, and ultimately, damage to the business’s reputation. Effective CRM software can provide a solution to these pervasive issues.
Key Features of a Small Business CRM
Three essential features for a small business CRM are contact management, sales pipeline management, and reporting and analytics. Contact management provides a centralized repository for all customer information, ensuring that everyone in the business has access to the most up-to-date details. This eliminates the risk of working with outdated or conflicting information, leading to more efficient and personalized interactions. Sales pipeline management allows businesses to track leads throughout the sales process, identifying bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement. Finally, robust reporting and analytics offer insights into customer behavior and sales performance, enabling data-driven decision-making to optimize strategies.
Scalability in CRM Software
Scalability is crucial for small businesses experiencing growth. As a business expands, its customer base grows, and its CRM system needs to adapt to handle the increased volume of data and interactions. A scalable CRM system can seamlessly accommodate this growth without requiring significant changes or costly upgrades. For example, a small bakery might initially use a CRM to manage its local customer base, but as it expands to multiple locations or introduces online ordering, the CRM should be able to scale to accommodate the increased data volume and complexity without requiring a complete system overhaul. This ensures continued efficiency and avoids the disruption associated with migrating to a new system.
Customer Journey Flowchart within a Small Business CRM
The following describes a simplified flowchart illustrating the customer journey within a small business CRM system. Imagine a customer interacting with a fictional company, “Cozy Candles.”
The flowchart begins with a New Lead entering the system, perhaps through a website contact form or a trade show. This lead’s information is then added to the CRM’s contact management system. Next, the lead progresses to the Qualification stage, where the sales team assesses their needs and potential. If qualified, the lead moves to the Proposal stage where a personalized offer is created and sent. Following a successful proposal, the lead becomes a Customer. Ongoing interactions, such as order updates and support requests, are recorded in the CRM. Finally, the customer may become a Repeat Customer leading to increased loyalty and revenue. The system then provides valuable data on customer lifetime value, purchase frequency, and other key metrics, allowing Cozy Candles to personalize marketing efforts and improve customer retention. This cyclical process highlights the value of a well-integrated CRM system in managing the entire customer lifecycle.
Exploring CRM Software Options
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for small businesses seeking to streamline operations and improve customer relationships. This section will explore different CRM options, comparing their features, costs, and security implications to help you make an informed decision. We’ll also examine the differences between free and paid versions and highlight successful small business CRM implementations.
Cloud-Based CRM vs. On-Premise CRM
Small businesses often face a critical decision: cloud-based or on-premise CRM? This table compares key aspects of each to aid in this choice.
| Feature | Cloud-Based CRM | On-Premise CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. | Accessible only from within the business’s network. |
| Cost | Typically subscription-based, with varying costs depending on features and users. Lower upfront investment. | Higher upfront investment in software licenses and hardware. Ongoing maintenance costs. |
| Maintenance | Vendor handles updates, maintenance, and security patches. | Requires dedicated IT staff or outsourcing for maintenance and updates. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to accommodate business growth. | Scaling requires significant investment in additional hardware and software. |
| Security | Security is the responsibility of the vendor, though data breaches can still occur. | Security is the responsibility of the business. Requires robust internal security measures. |
Popular CRM Software Options for Small Businesses
Several CRM platforms cater specifically to the needs of small businesses, offering varying features and pricing structures. Choosing the right one depends on your specific requirements and budget.
Below are five popular options, along with examples of their pricing tiers (note that pricing can change, so always check the vendor’s website for the most up-to-date information):
- HubSpot CRM: Offers a robust free version with limited features and paid plans starting around $450/month for more advanced functionalities.
- Zoho CRM: Provides a free plan with basic features and various paid plans ranging from approximately $14/user/month to $50/user/month depending on features and users.
- Salesforce Essentials: A simplified version of Salesforce designed for small businesses. Pricing typically starts around $25/user/month.
- Freshsales: Offers a free plan with limited features and paid plans starting at around $12/user/month for more comprehensive capabilities.
- Pipedrive: Focuses on sales pipeline management. Pricing starts around $12.50/user/month for essential features, with higher tiers for more advanced features.
Free vs. Paid CRM Software
The key differences between free and paid CRM software often revolve around functionality, support, and scalability. Free versions typically offer limited features, user support, and storage capacity. Paid versions unlock more advanced features, better customer support, and increased storage, enabling businesses to scale their operations more effectively. For instance, a free CRM might offer basic contact management, while a paid version would include features like sales pipeline management, marketing automation, and reporting dashboards. The choice depends on the current and future needs of the business.
Successful Small Business CRM Implementations
Successful CRM implementation requires careful planning and execution. For example, a local bakery might use a CRM to manage customer orders, track preferences, and send personalized marketing emails. This approach improves customer loyalty and drives repeat business. Similarly, a small consulting firm could leverage a CRM to track projects, manage client interactions, and improve team collaboration, ultimately boosting efficiency and client satisfaction. The key is to choose a CRM that aligns with the specific business needs and to invest time in proper training and data entry to maximize its benefits.
Implementing and Managing a CRM System
Successfully implementing a CRM system requires careful planning and execution. A phased approach, focusing on user training and data migration, minimizes disruption and maximizes the system’s benefits for your small business. This section details the key steps involved in a smooth transition and ongoing management.
Step-by-Step CRM Implementation Guide
Implementing a new CRM system involves several key steps. A well-defined plan ensures a smooth transition and minimizes disruption to daily operations. Consider this a roadmap for a successful implementation.
- Needs Assessment and System Selection: This initial phase, already covered, involves identifying your business’s specific needs and choosing a CRM system that aligns with those requirements. This includes considering features, scalability, and budget.
- Data Migration: Transferring existing customer data from legacy systems to the new CRM is crucial. This process requires careful planning and potentially the use of data migration tools to ensure data integrity and accuracy. Thoroughly check and clean data before importing.
- System Configuration and Customization: Configure the CRM to match your business processes. This may involve customizing workflows, fields, and reports to optimize efficiency. Consider involving key users in this process to ensure the system meets their needs.
- User Training and Onboarding: Comprehensive training is vital for successful CRM adoption. Provide both initial training and ongoing support to empower employees to utilize the system effectively. Hands-on training sessions and readily available documentation are beneficial.
- Go-Live and Initial Monitoring: Launch the CRM system and closely monitor its performance. Address any immediate issues and collect feedback from users to identify areas for improvement. Regular system checks and data backups are crucial.
- Ongoing Optimization and Maintenance: Regularly review and refine your CRM strategy. This includes updating processes, adding new features, and adapting to changing business needs. Consider scheduled maintenance and software updates to ensure optimal performance.
Integrating CRM with Existing Business Tools
Seamless integration with existing tools significantly enhances the value of your CRM system. For example, integrating your CRM with email marketing platforms allows for targeted campaigns based on customer segmentation.
- Email Marketing Integration: Integrating with platforms like Mailchimp or Constant Contact allows for personalized email marketing campaigns based on customer data within the CRM. This improves customer engagement and ROI.
- Accounting Software Integration: Connecting your CRM to accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero) automates invoicing, tracks payments, and provides a complete view of customer financial interactions. This streamlines financial processes and reduces manual data entry.
- E-commerce Platform Integration: If you operate an online store, integrating your CRM with your e-commerce platform provides a holistic view of customer interactions, from browsing to purchase and beyond. This allows for personalized recommendations and targeted marketing.
Data Security and Privacy in CRM Systems
Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount. Data breaches can severely damage your business’s reputation and lead to legal repercussions.
Implementing robust security measures, such as strong passwords, access controls, and regular data backups, is essential. Compliance with relevant data privacy regulations (like GDPR or CCPA) is also crucial. Regular security audits and employee training on data security best practices are highly recommended. Consider encryption for data both in transit and at rest.
Sample CRM Training Plan for Small Business Employees
Effective training ensures employees confidently use the CRM system. A structured plan promotes consistent usage and maximizes the system’s benefits.
| Week | Training Topic | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CRM Introduction and Basic Navigation | Interactive presentation, guided tour of the system interface, Q&A session |
| 2 | Data Entry and Management | Hands-on exercises, role-playing scenarios, practice with real or sample data |
| 3 | Reporting and Analytics | Generating reports, interpreting data, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) |
| 4 | Advanced Features and Customization | Exploring advanced features, customizing workflows and dashboards, addressing specific user needs |
| 5 | Ongoing Support and Best Practices | Open forum, troubleshooting sessions, sharing best practices and tips |
Measuring CRM Success
Implementing a CRM system is only half the battle; understanding its effectiveness is crucial for maximizing return on investment. Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) allows small businesses to gauge the impact of their CRM on sales, customer satisfaction, and overall operational efficiency. Regular monitoring and analysis of this data enable informed decisions, leading to continuous improvement and stronger customer relationships.
Key Performance Indicators for CRM Success
Three key performance indicators provide a comprehensive overview of CRM effectiveness in a small business context. These metrics offer insights into sales performance, customer engagement, and operational efficiency, allowing for targeted improvements.
| KPI | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Measures the cost of acquiring a new customer. A lower CAC indicates greater efficiency in marketing and sales efforts. | If a company spends $1000 on marketing and acquires 10 new customers, the CAC is $100. A decrease in CAC suggests improved targeting or more effective marketing campaigns. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | Predicts the total revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the business. A higher CLTV indicates stronger customer loyalty and retention. | If a customer spends an average of $500 annually for 5 years, the CLTV is $2500. Increasing CLTV requires strategies focusing on customer retention and upselling/cross-selling. |
| Sales Cycle Length | Tracks the time it takes to convert a lead into a paying customer. A shorter sales cycle indicates improved sales efficiency and streamlined processes. | A reduction from an average of 3 months to 2 months demonstrates the effectiveness of CRM-driven improvements in lead nurturing and sales processes. |
CRM Dashboard Design
A well-designed dashboard provides a clear and concise overview of these KPIs, allowing for quick identification of trends and areas for improvement.
| KPI | Metric | Target | Current Value | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | $100 | <$90 | $110 | Increasing |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | $2500 | >$3000 | $2200 | Decreasing |
| Sales Cycle Length | 60 days | <45 days | 75 days | Increasing |
This dashboard allows for easy monitoring of each KPI against pre-defined targets. The trend column highlights whether the KPI is improving or worsening, facilitating prompt intervention where necessary.
Analyzing CRM Data for Improvement
Analyzing CRM data involves more than just observing numbers; it’s about understanding the “why” behind the trends. This requires examining data patterns, identifying correlations, and drawing actionable insights. For example, analyzing customer demographics linked to CLTV can reveal which customer segments are most valuable, informing targeted marketing and retention strategies. Similarly, analyzing sales cycle length in conjunction with lead source can highlight the most effective channels for generating high-quality leads.
Examples of CRM Reports
CRM systems generate a variety of reports to track progress towards business goals. These reports provide detailed insights into various aspects of business performance.
* Sales Performance Report: Tracks sales revenue, conversion rates, and sales representative performance. This helps identify top performers, areas needing improvement, and successful sales strategies.
* Customer Segmentation Report: Groups customers based on shared characteristics (demographics, purchase history, engagement level). This facilitates targeted marketing campaigns and personalized customer experiences.
* Lead Source Report: Identifies the sources that generate the most qualified leads, allowing for optimized resource allocation and improved marketing ROI.
* Customer Churn Report: Tracks customer attrition rates and identifies reasons for churn. This helps develop strategies to improve customer retention and reduce churn.
Future Trends in Small Business CRM
The landscape of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting business needs. Small businesses, often operating with limited resources, need to understand these trends to leverage the power of CRM effectively and remain competitive. Failing to adapt could mean missing out on crucial opportunities for growth and customer satisfaction.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and other emerging technologies is reshaping the CRM experience for small businesses, offering both exciting possibilities and potential challenges.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Small Business CRM
AI is rapidly transforming CRM software, moving beyond simple automation to offer more intelligent and personalized customer interactions. AI-powered CRM systems can analyze vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns, predict future behavior, and automate tasks such as lead scoring, customer segmentation, and personalized email marketing. For example, a small bakery could use AI to analyze customer purchase history and preferences to predict demand for specific items, optimizing inventory management and reducing waste. This also allows for proactive customer service, anticipating needs before customers even express them. AI chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human employees to focus on more complex issues. The result is increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and better resource allocation.
Emerging Technologies Influencing Small Business CRM
Several emerging technologies are poised to significantly impact the future of small business CRM.
- Predictive Analytics: Going beyond basic reporting, predictive analytics uses AI and machine learning to forecast customer behavior, enabling proactive sales and marketing strategies. A clothing boutique, for example, might use predictive analytics to anticipate seasonal trends and adjust inventory accordingly.
- Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA automates repetitive tasks, freeing up employees for more strategic work. This could involve automating data entry, appointment scheduling, or even generating basic customer reports.
- Integration with other business tools: Seamless integration with accounting software, e-commerce platforms, and marketing automation tools provides a holistic view of the customer journey and streamlines operations. Imagine a small online retailer seamlessly integrating their CRM with their shipping platform, allowing for automated order updates and tracking information directly within the CRM system.
- Mobile-first CRM: With the increasing reliance on mobile devices, CRM systems need to be accessible and functional across all platforms. This ensures employees can access customer information and manage interactions regardless of their location.
Challenges in Adapting to Future Trends
While the potential benefits are significant, small businesses face challenges in adopting these new technologies.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining AI-powered CRM systems can be expensive, particularly for businesses with limited budgets. Careful consideration of ROI is crucial.
- Data Security and Privacy: The increased reliance on data necessitates robust security measures to protect sensitive customer information and comply with relevant regulations like GDPR.
- Lack of Expertise: Small businesses may lack the in-house expertise to implement and manage complex AI-driven CRM systems, potentially requiring external consultants or training.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating new technologies with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and execution.
Outlook on the Future of Small Business CRM
The future of CRM for small businesses is bright, with AI and other technologies offering immense potential for growth and improved customer relationships. However, careful planning, investment, and a focus on data security are essential for successful adoption. Businesses that embrace these changes stand to gain a significant competitive advantage, while those that fail to adapt risk being left behind. The key lies in choosing the right tools, understanding their limitations, and prioritizing employee training to maximize their effectiveness. The risks are mainly associated with cost, security, and integration challenges, but the potential rewards—enhanced customer relationships, streamlined operations, and data-driven decision-making—far outweigh these hurdles for businesses willing to invest the time and resources.
Final Conclusion
Ultimately, the right CRM software can transform how a small business interacts with its customers, leading to increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced profitability. By carefully considering your needs, exploring available options, and implementing a well-defined strategy, you can harness the power of CRM to drive your small business towards lasting success. Remember, the key is to select a system that aligns with your current needs while offering the scalability to accommodate future growth.